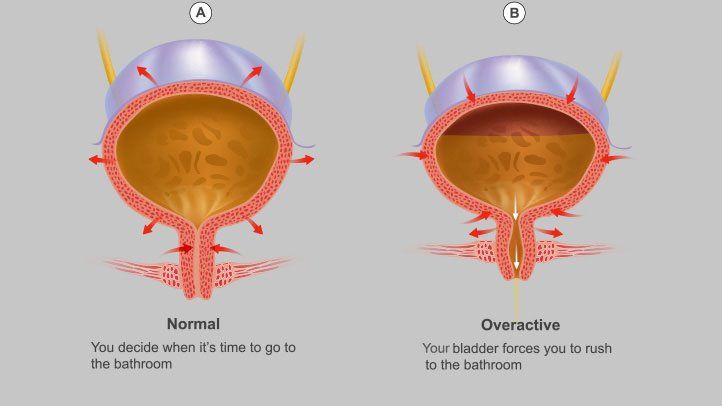
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a medical condition characterized by a frequent and urgent need to urinate. It can be accompanied by involuntary urine leakage (urge incontinence) and often disrupts daily life. Here’s an overview of OAB, its causes, symptoms, and common treatment options:
Causes:
The exact cause of overactive bladder is often unclear, but it may result from a combination of factors, including:
- Muscle and Nerve Dysfunction: Problems with the bladder’s muscles or nerves can lead to abnormal contractions and a frequent urge to urinate.
- Bladder Infections: Infections or irritation of the bladder can cause temporary symptoms of OAB.
- Bladder Stones: The presence of bladder stones can lead to OAB-like symptoms.
- Bladder Tumors: In rare cases, tumors in the bladder can cause OAB symptoms.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can irritate the bladder or affect its function, leading to OAB symptoms.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, multiple sclerosis, or Parkinson’s disease can affect nerve signals to the bladder and contribute to OAB.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of overactive bladder include:
- Frequent urination (more than eight times a day).
- Urgency to urinate, often with little warning.
- Nocturia, or waking up at night to urinate.
- Urge incontinence, which involves involuntary urine leakage after a sudden, intense urge to urinate.
- Feelings of frustration, anxiety, or embarrassment related to these symptoms.
Treatment:
The treatment of overactive bladder typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, behavioral therapies, and, in some cases, medication or medical procedures:
Behavioral Therapies:
- Bladder Training: A healthcare provider or Urologist in Karachi may recommend scheduled voiding to help retrain the bladder and reduce the frequency and urgency of urination.
- Scheduled Toileting: Establishing a regular bathroom schedule can help manage symptoms.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegel exercises): Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can improve bladder control and reduce urgency and leakage.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes: Reducing caffeine, alcohol, and acidic foods in your diet can help alleviate symptoms.
- Hydration Management: Adjusting your fluid intake, particularly in the evening, can help reduce nighttime urination.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can relieve pressure on the bladder.
Medications:
- Various prescription medications, including anticholinergic drugs and beta-3 agonists, can help relax the bladder and reduce OAB symptoms.
Surgery:
- In rare cases when other treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions such as bladder augmentation or urinary diversion may be considered.
It’s essential to consult a Best Urologist in Lahore if you are experiencing OAB symptoms. They can assess your condition, recommend appropriate treatments, and help you manage the condition effectively to improve your quality of life.